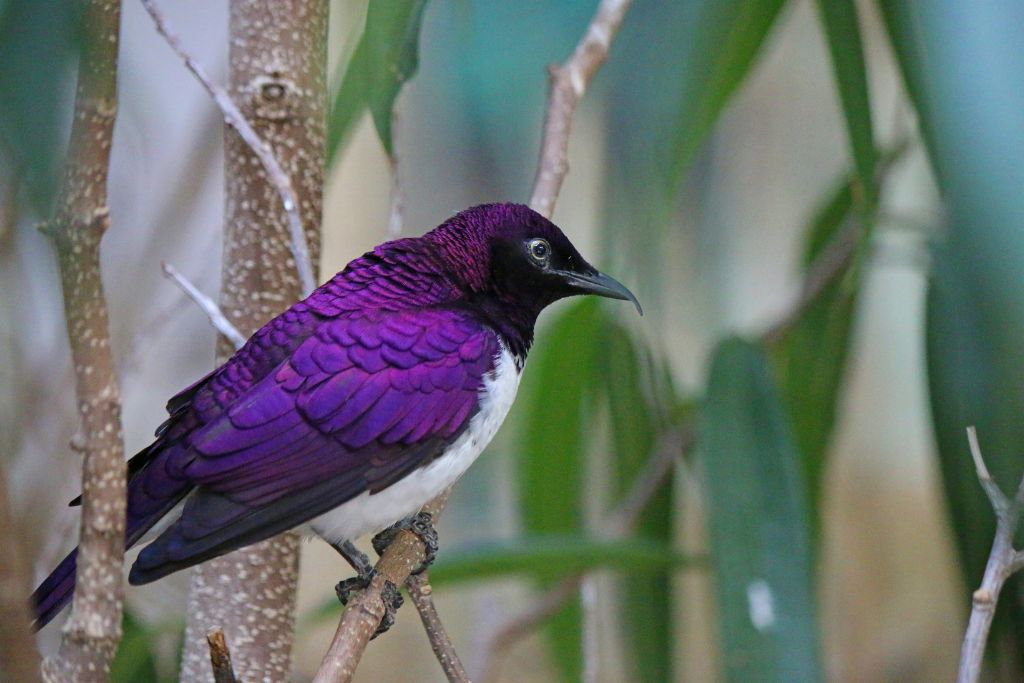
Have you ever thought about how fascinating purple birds and their bright feathers are? Think about this: 26 different species, each with its own unique purple pattern. But why is it purple? What makes these birds stand out in a world of different colors? Let’s discover the world of these winged beauties and find out how their beautiful colors are made.
Purple birds, from dark violet to light lavender, show how beautiful nature is. There are different reasons why birds like the violet-crowned woodnymph and the purple emperor butterfly show their colors. Sometimes, they use their bright feathers to hide in the wild, and other times, to attract mates.
More than just being pretty, birds are good for the environment. These amazing birds spread seeds, which makes plants more diverse. Many birds are very good at hunting bugs, which is a healthy way to get rid of pests. Learn about the intricate web of purple bird species and understand how important birds are to landscapes worldwide.
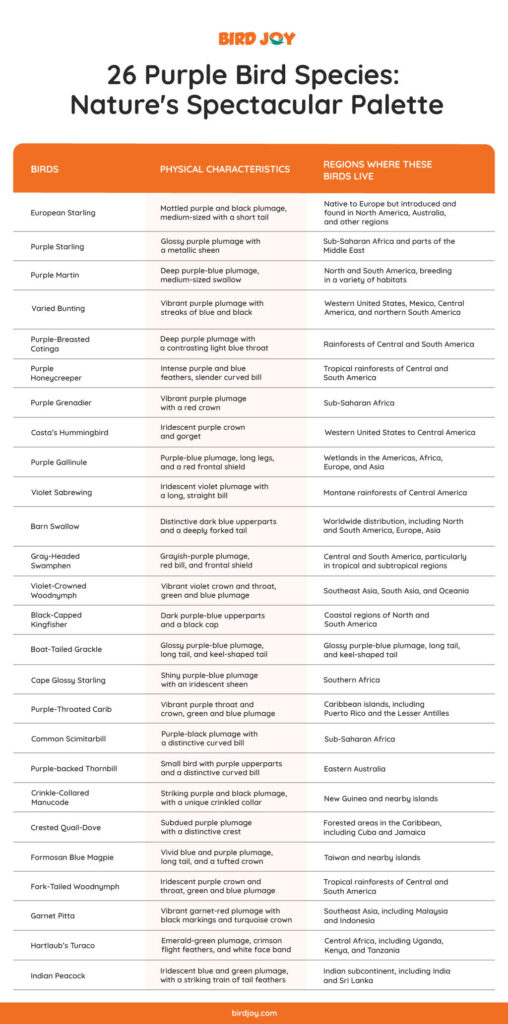
Discovering 26 Birds That are Purple
Purple birds have stunning plumage of deep violets and gentle lavenders. What makes these birds special, and how do they enrich our ecosystems? Let’s explore purple birds’ magical world and learn their intriguing tales.
1. European Starling (Sturnus vulgaris)
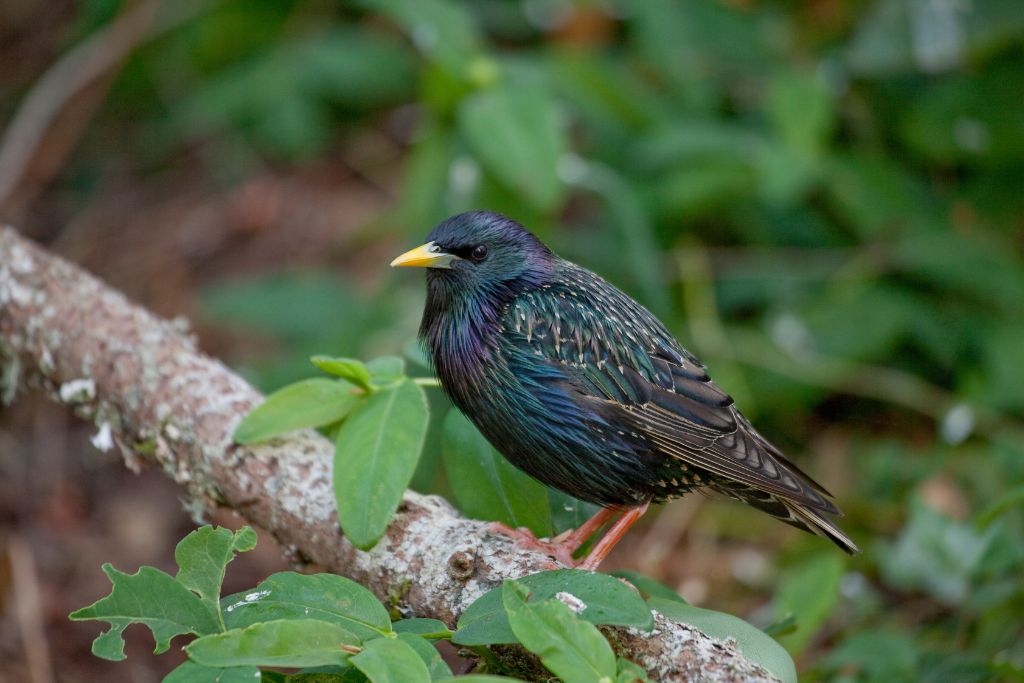

The European starling is a small bird with shiny black and purple feathers and white spots. They may change their calls to sound like car sirens and other birds. They do well in cities, fields, and forests in North America, Europe, and Asia. These adaptable birds became one of the most common kinds in North America after being brought there in the 1800s.
2. Purple Starling (Lamprotornis purpureus)
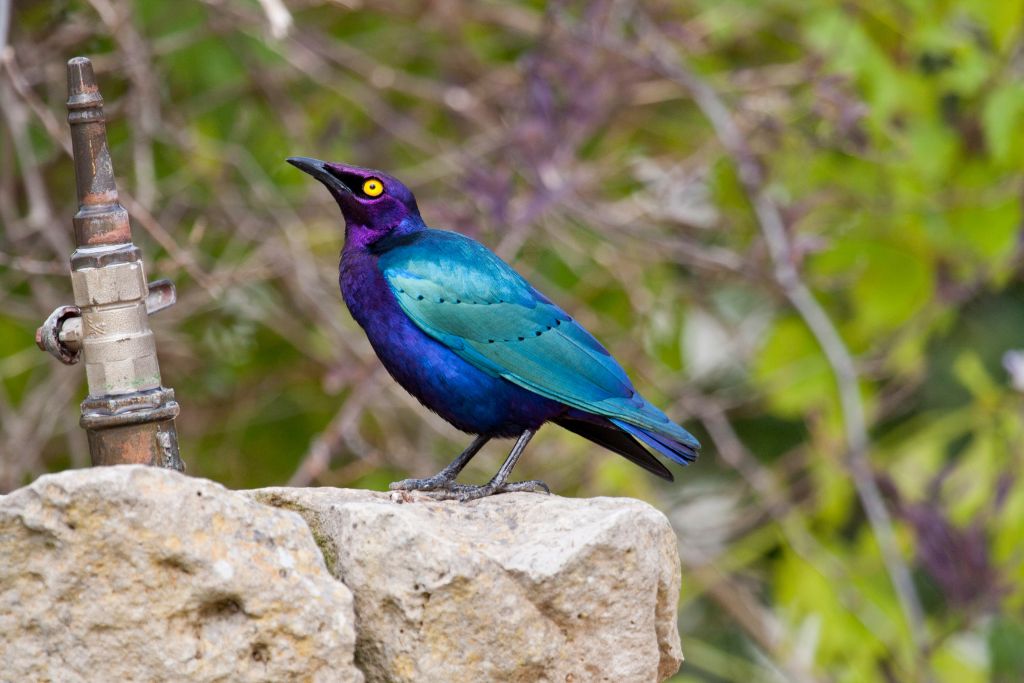

The purple starling has a stunning purple plumage that sparkles in the sun. These East African starlings have stunning iridescence. These gregarious birds assemble in big groups and have melodic calls. Purple starlings help plants flourish in savannahs, woods, and grasslands by dispersing seeds.
3. Purple Martin (Progne subis)
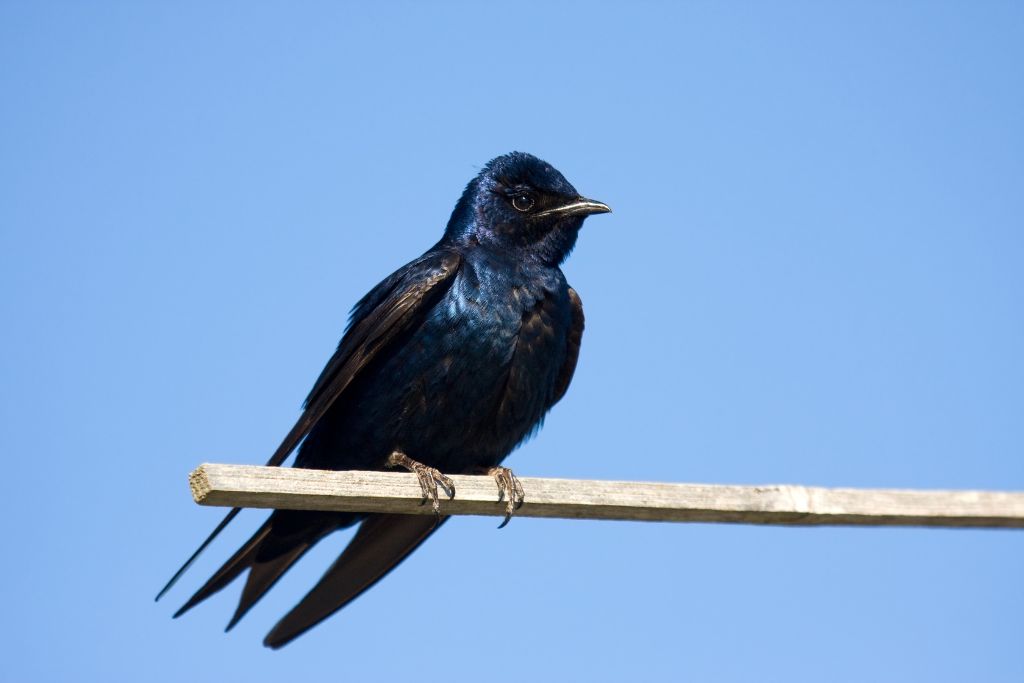

It’s a pretty bird with bright purple feathers that sings happily. Birdwatchers love these North American migratory birds because they nest in homes that have been carefully built for them. They like open areas near water where they can catch flying insects as their food. They keep bugs away and look nice, which is very important to the environment.
4. Varied Bunting (Passerina versicolor)

The little varied bunting has brilliant purple, blue, and scarlet plumage. These tiny birds move quickly between plants and trees. In the Southern US and Mexico, brushy, open woodlands and grasslands are preferred. Male buntings display a rainbow of colors to lure mates during breeding season.
5. Purple-Breasted Cotinga (Cotinga cotinga)
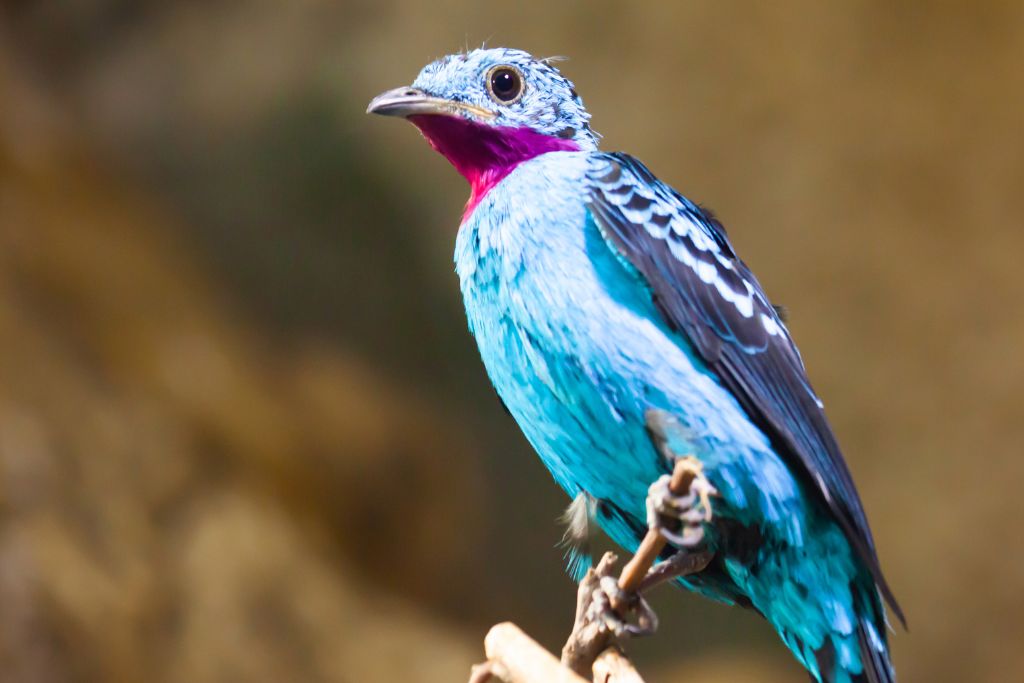

The tropical purple-breasted cotinga features deep purple plumage and an electric blue throat. These Central and South American birds court with acrobatic flights and sweet cries. Their preferred habitat is the rainforest canopy because it supplies many fruits, their major food. This bird seed dispersal aids rainforest restoration.
6. Purple Honeycreeper (Cyanerpes caeruleus)
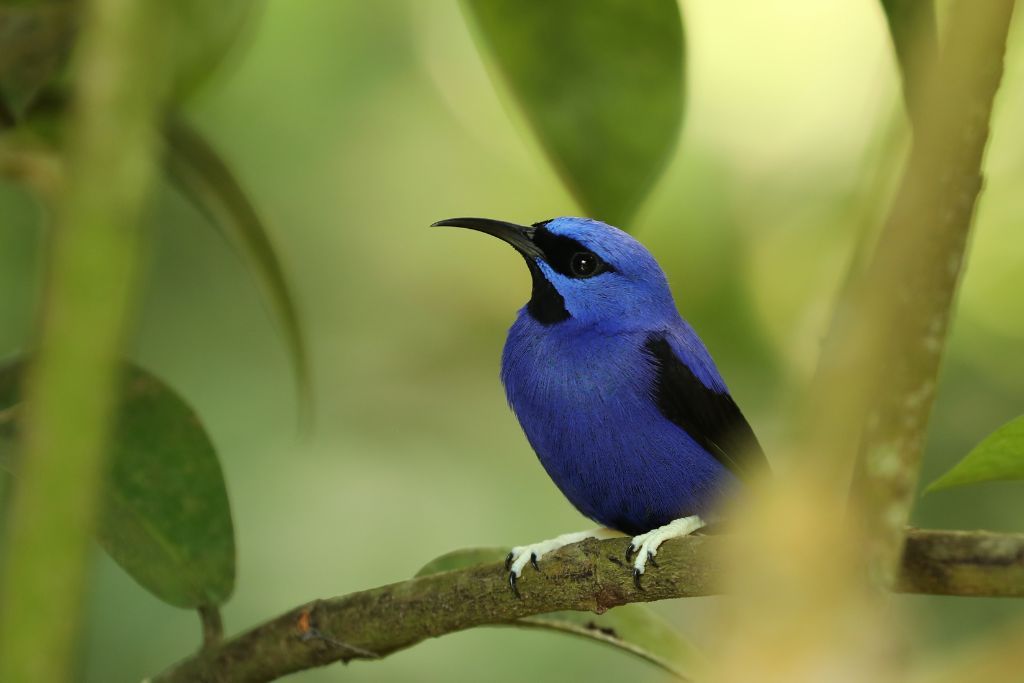

Discover the little purple honeycreeper with its purple and turquoise plumage. These Central and South American gems dwell in tropical forests. Males are vividly colorful, females greenish. Long-billed purple honeycreepers pollinate plants and help them reproduce. As they soar from flower to flower, these birds beautify and enrich their lush environments.
7. Purple Grenadier (Granatina ianthinogaster)
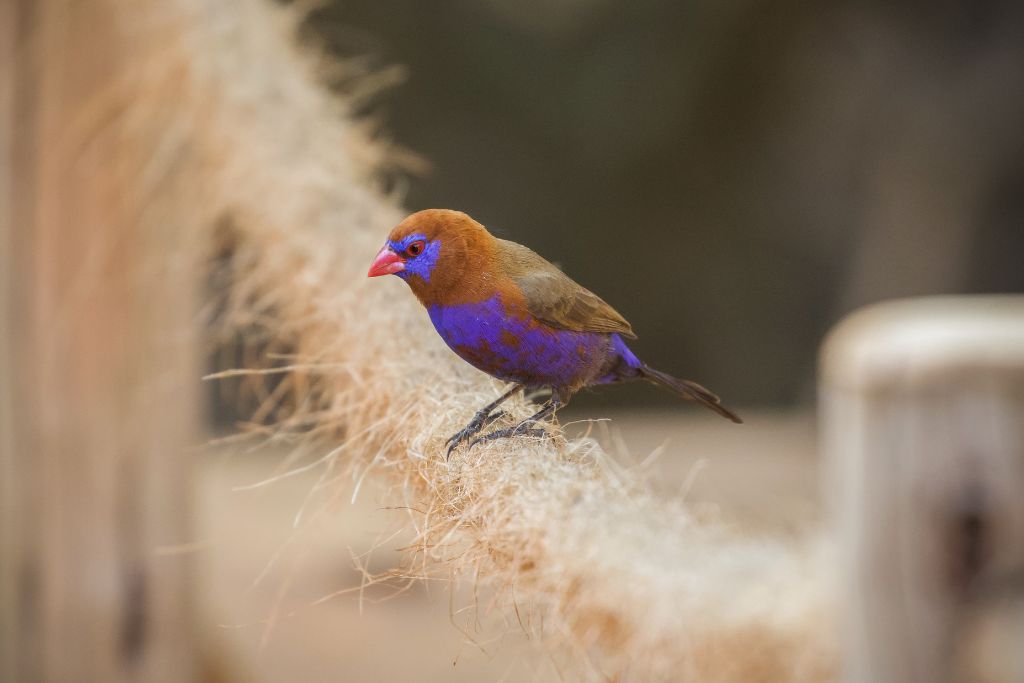

Purple grenadier is a Sub-Saharan African bird. Males of this species have remarkable purple plumage with red shoulder patches. These social birds forage for seeds and insects in open forests and savannahs in flocks. Male purple grenadiers do aerial acrobatics during courtship to lure mates. These birds brighten their surroundings and disperse seeds by eating various plants.
8. Costa’s Hummingbird (Calypte costae)
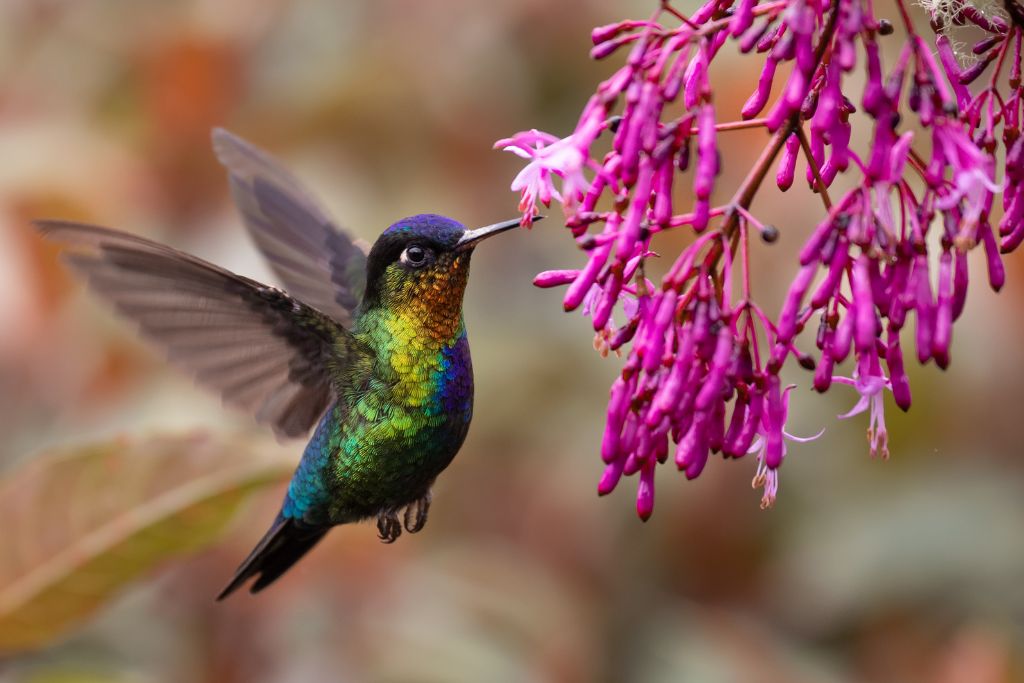

These birds are agile flyers from the Southwestern US and Mexico. It has vibrant purple plumage on the male’s throat and head. Long bills collect nectar from flowers as they hover with a high wingbeat rate. These little birds stage astonishing airborne feats in intricate courtship rituals to lure mates.
9. Purple Gallinule (Porphyrio martinicus)
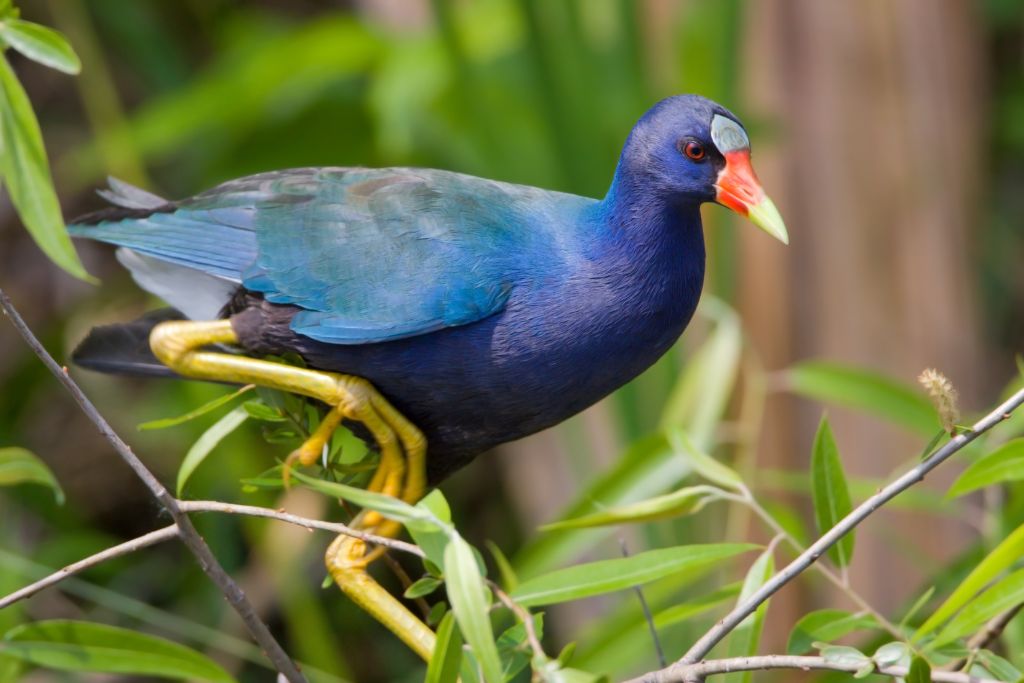

Purple gallinules are beautiful birds of American marshes and wetlands. This aquatic bird stands out with its purple-blue plumage, scarlet beak, and long legs. Large feet let purple gallinules walk on lily pads and swim easily. They inhabit tropical and subtropical regions from the Southeastern US to South America. These birds are adapted to various wetland settings because they can create floating nests in dense foliage. The purple gallinule’s appearance and behavior intrigue birdwatchers and environment lovers.
10. Violet Sabrewing (Campylopterus hemileucurus)
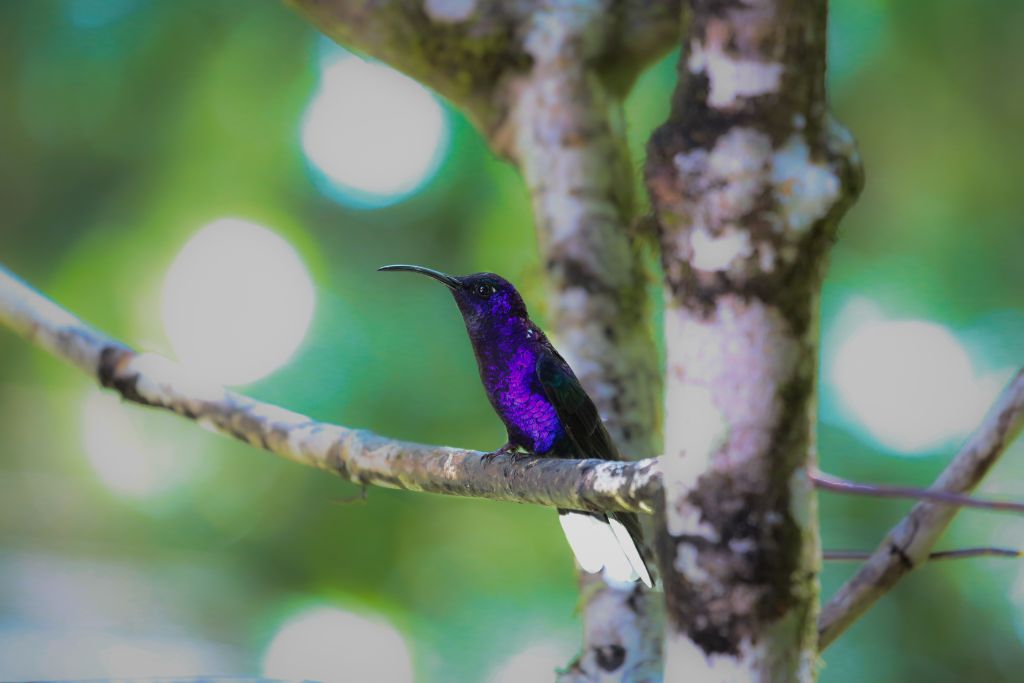

This beautiful hummingbird lives in Central America and is called the violet sabrewing. The throat and belly of this bird have big, bright violet feathers that make it stand out. During the breeding season, male violet sabrewings use their quick-flight and long, saber-like wings to put on shows to draw females. Montane and tropical rainforests are their home, where they eat flower nectar. These hummingbirds pollinate many plant species in their environments.
11. Barn Swallow (Hirundo rustica)

Barn swallows are common and agile birds with forked tails. They are airborne acrobats that collect insects. They build cup-shaped nests under eaves or on ledges in farms, fields, and cities. Their incredible migration of thousands of miles between Northern Hemisphere breeding grounds and Southern Hemisphere wintering areas is fascinating.
12. Gray-Headed Swamphen (Porphyrio poliocephalus)
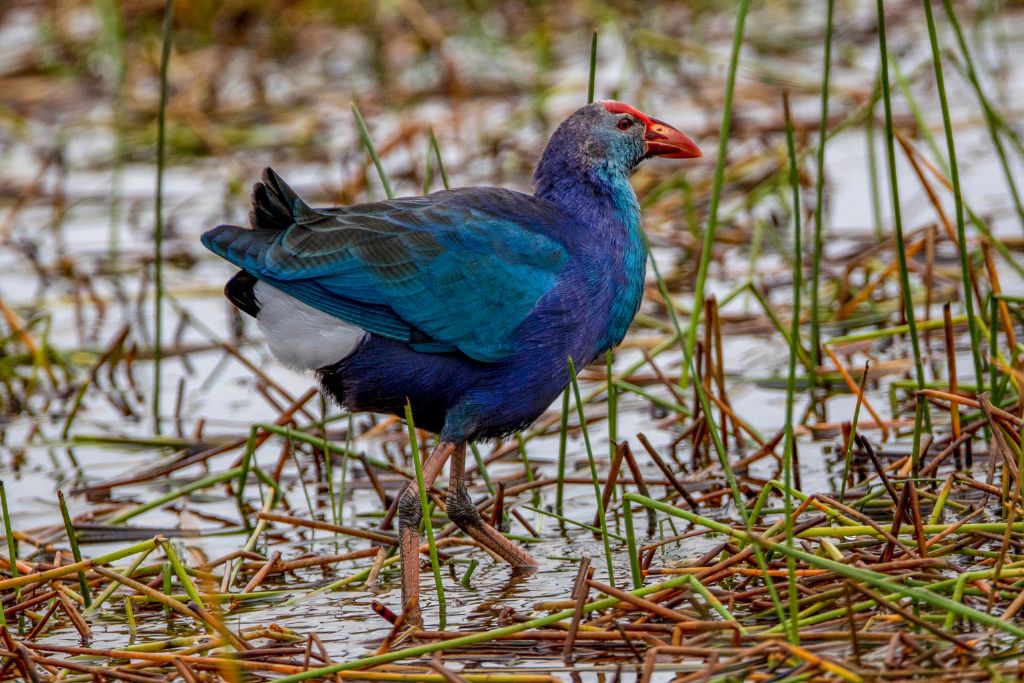

These birds have gray heads and necks and stunning blue and purple plumage. These waterfowl swim and walk well in marshes, wetlands, and freshwater. They use their large toes to explore floating plants and nest in reeds. Booming gray-headed swamphens are native to Australia and Asia. Wetland communities benefit from these birds’ territoriality and duets.
13. Violet-Crowned Woodnymph (Thalurania colombica)
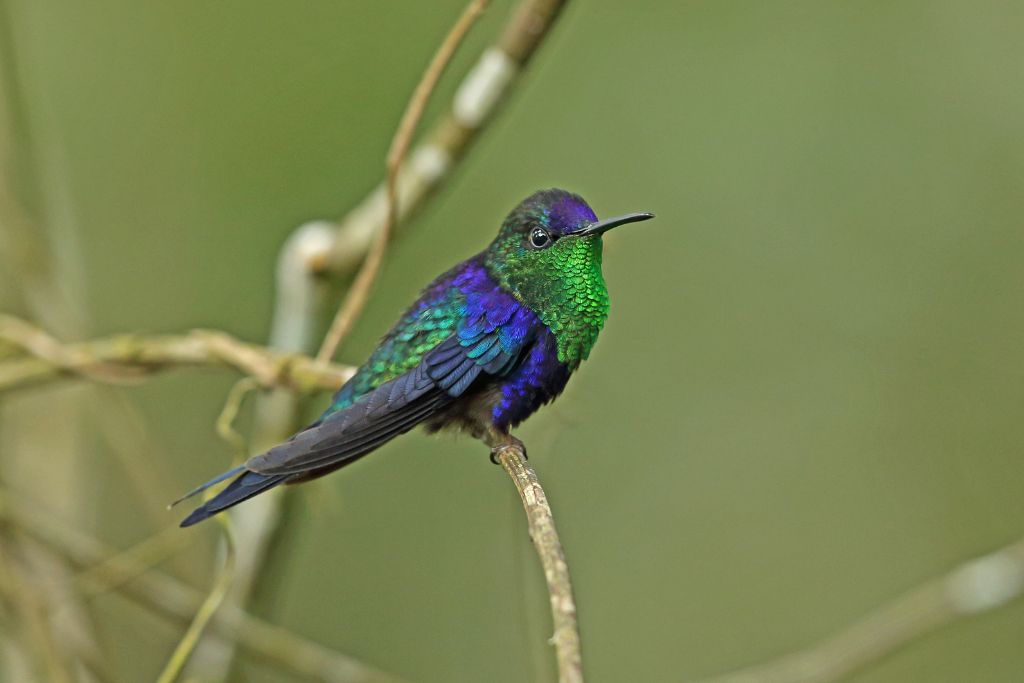

A violet-crowned woodnymph is a beautiful Central and South American hummingbird. Male woodnymphs are attractive with their violet heads and bright green plumage. Flying fast and territorial, they attract mates. Tropical and subtropical hummingbirds eat garden and woodland flowers. In specific settings, the violet-crowned woodnymph pollinates many plant kinds.
14. Black-Capped Kingfisher (Halcyon pileata)
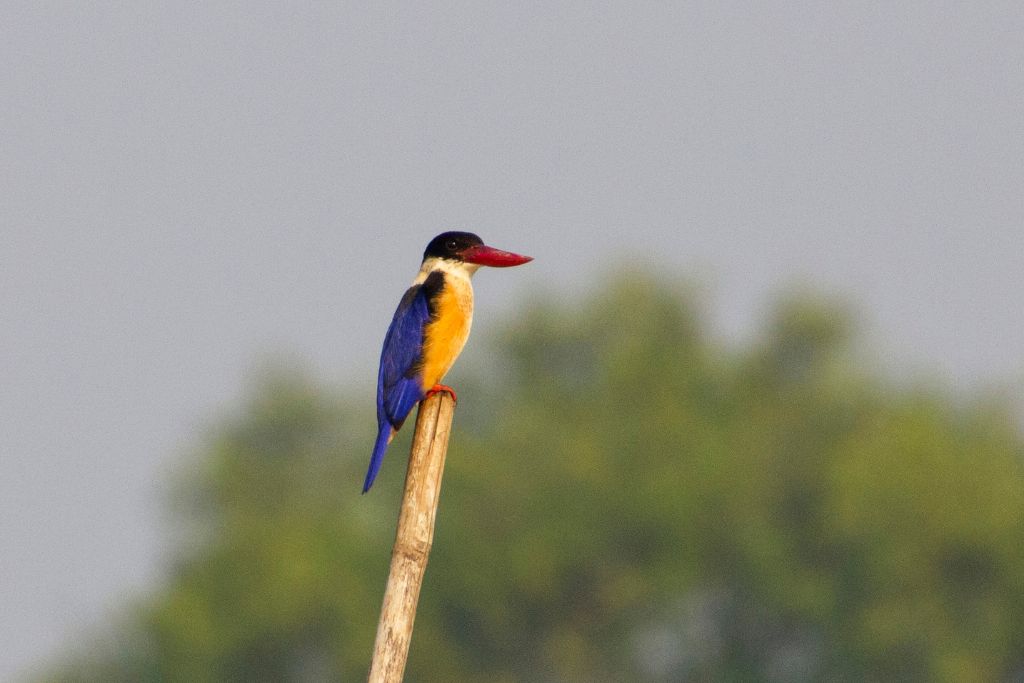

Black-capped kingfishers are beautiful black-and-white birds with blue crowns. Due to its fishing skills, this kingfisher is typically seen around lakes, rivers, and beaches. With its acute bill and good eyesight, it dives to grab fish and other aquatic prey. They occupy city ponds and water features. Solo kingfishers dive fast to get their prey.
15. Boat-Tailed Grackle (Quiscalus major)
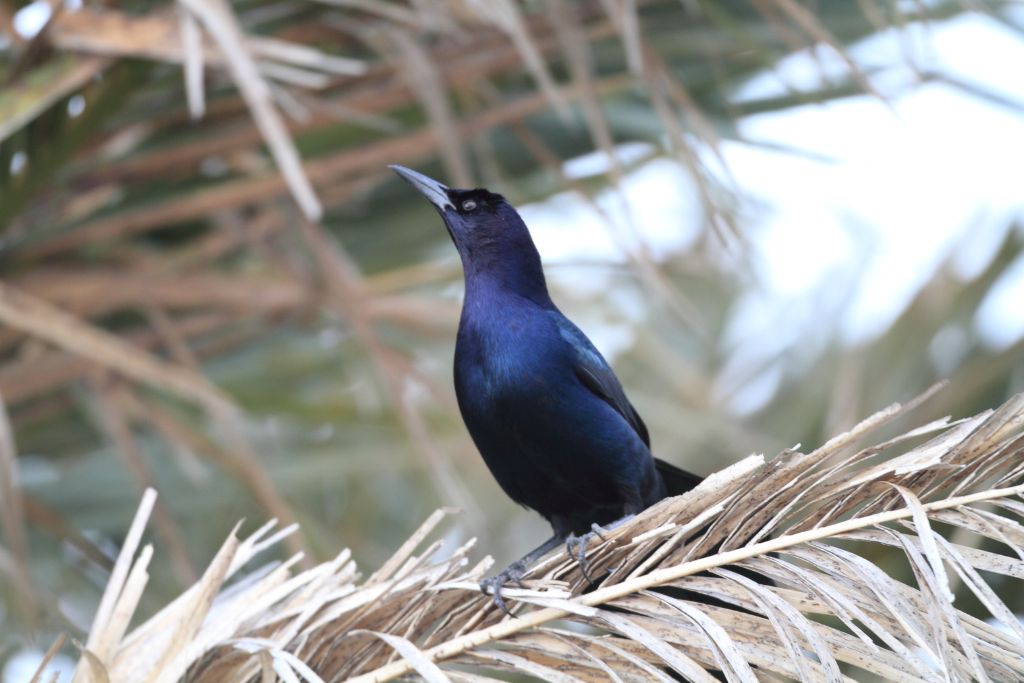

Long, keel-shaped tails and iridescent plumage identify North American boat-tailed grackles. During the breeding season, males have glossy black feathers with violet luster. In marshes, wetlands, and coastal areas, they hunt insects, tiny fish, and seeds. Males use vocalizations, feathers, and tails to attract mates. Large flocks of social grackles fill their habitats with sound.
16. Cape Glossy Starling (Lamprotornis nitens)
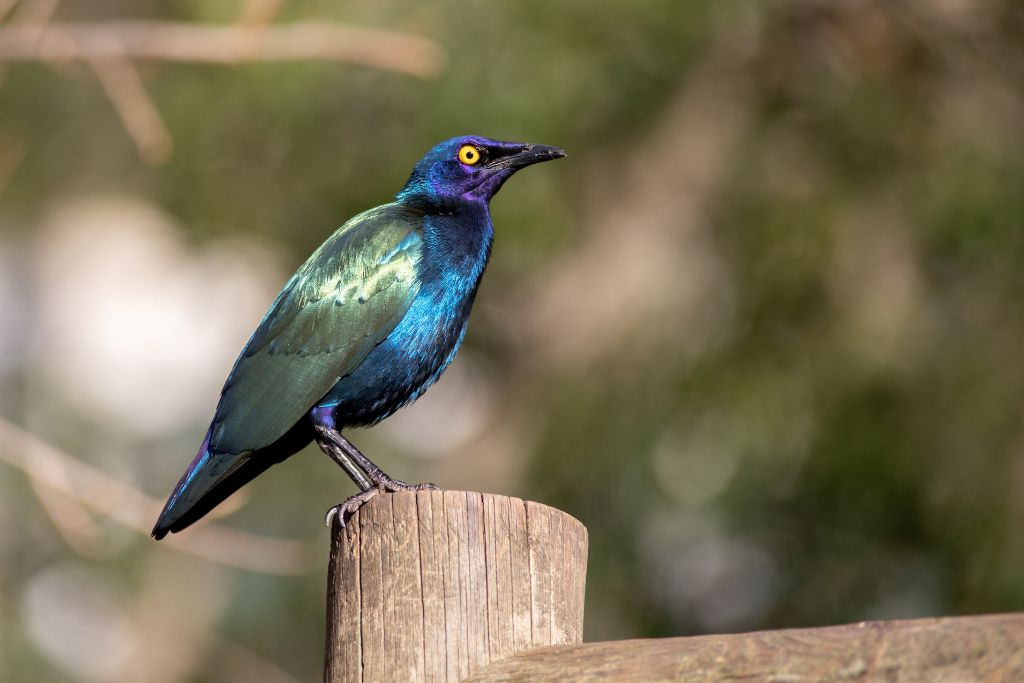

Its lustrous purple, blue, and green plumage makes this starling gorgeous. Savannah and grassland starlings gather in flocks to graze for insects and fruits. The cape glossy starling courted with elaborate vocalizations and soaring displays. Their glossy feathers are generated by structural coloration, where tiny features reflect and refract light to create sparkle.
17. Purple-Throated Carib (Eulampis jugularis)
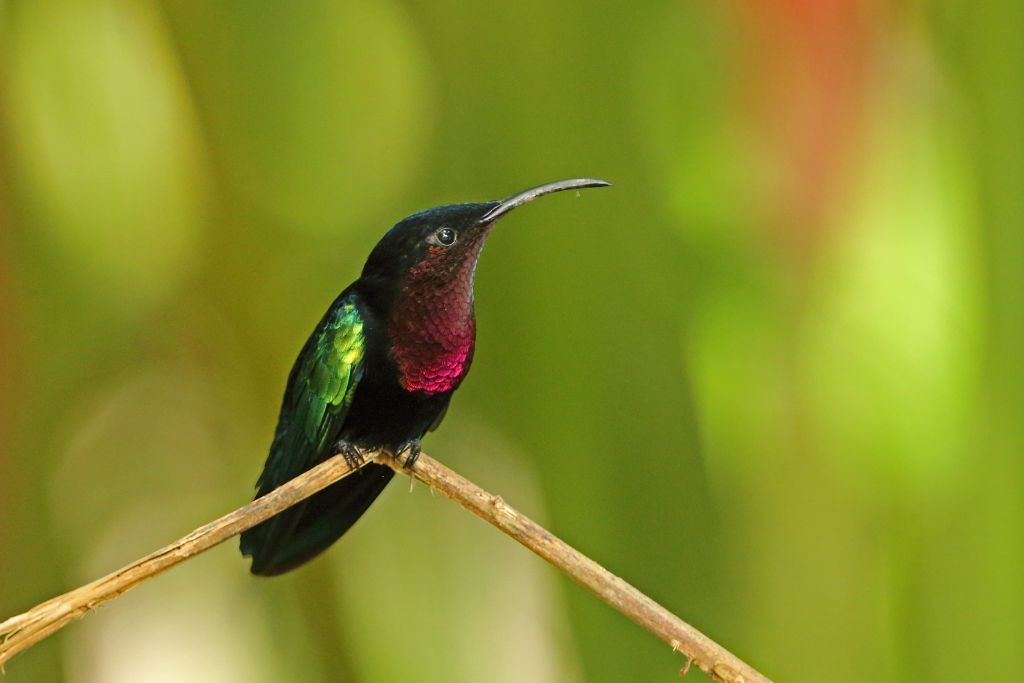

Female purple-throated carib are duller than males, with vivid iridescent green plumage and a purple throat. Their agile flight patterns let them loiter near flowers for nectar. During mating season, territorial purple-throated carib males execute aerial displays to attract partners. Hummingbirds pollinate tropical and subtropical plants.
18. Common Scimitarbill (Rhinopomastus cyanomelas)
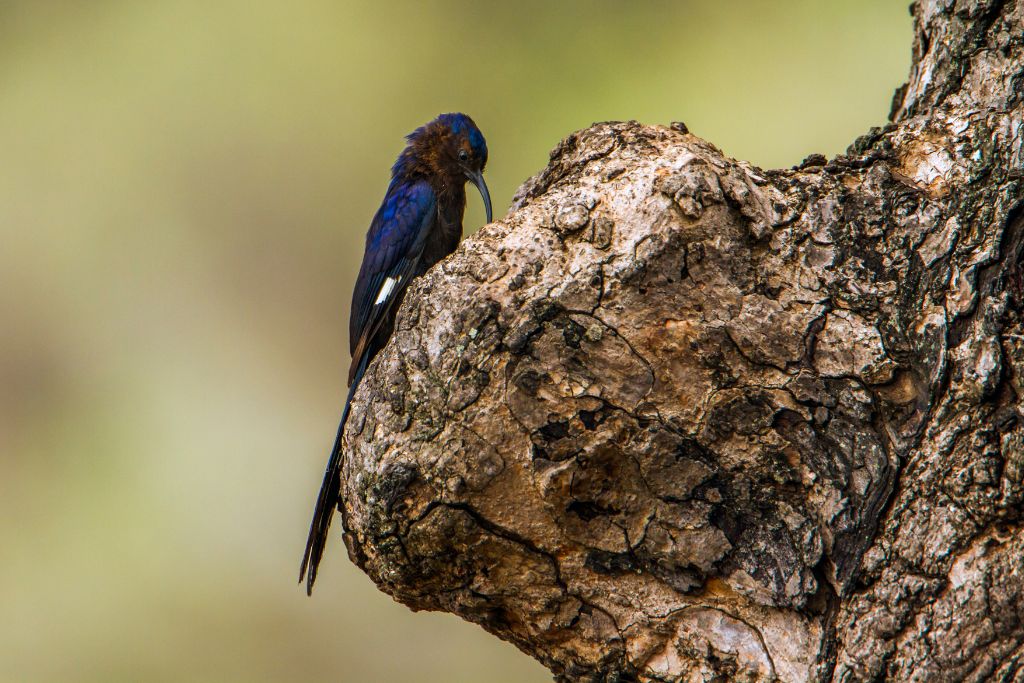

These Sub-Saharan African birds have remarkable black plumage and long, down-curved beaks. Common scimitarbills eat ground insects, reptiles, and small animals. With their bills, they hunt in mud and leaf litter in savannahs, grasslands, and forests. Monogamous common scimitarbills facilitate social dynamics in their ecosystem.
19. Purple-Backed Thornbill (Ramphomicron microrhynchum)
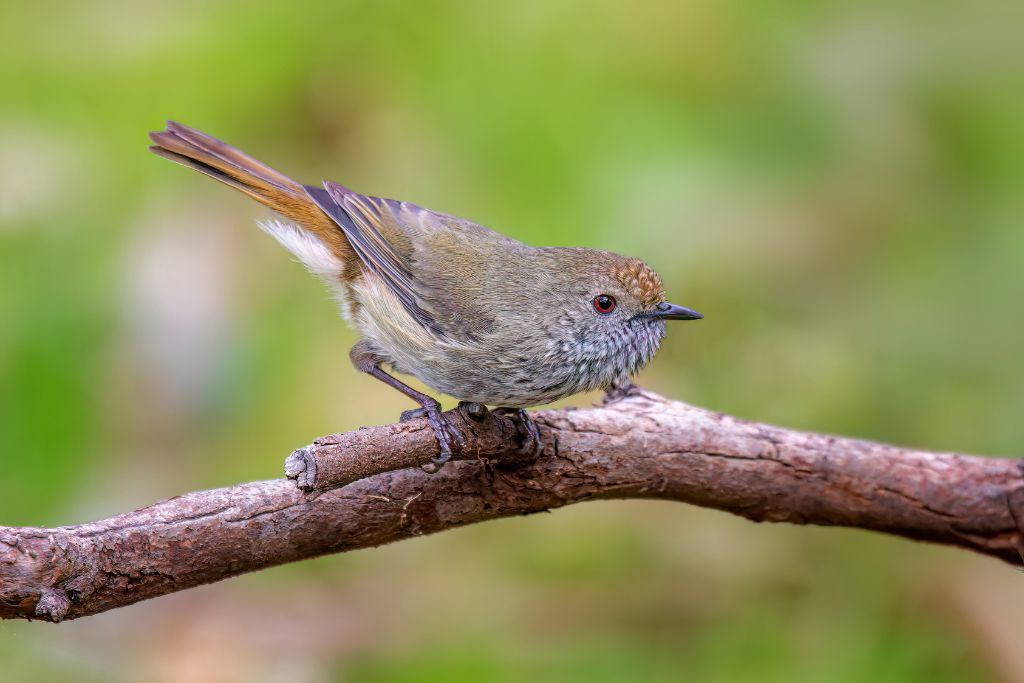

The shimmering green plumage and purple back patch make this bird appealing in high-altitude cloud forests. The purple-backed thornbill stays near flowers to eat nectar and flies fast. Hummingbirds feed upside-down from flowers, unusually. Mountains are linked to these birds’ pollination of high-altitude vegetation.
20. Crinkle-Collared Manucode (Manucodia chalybatus)
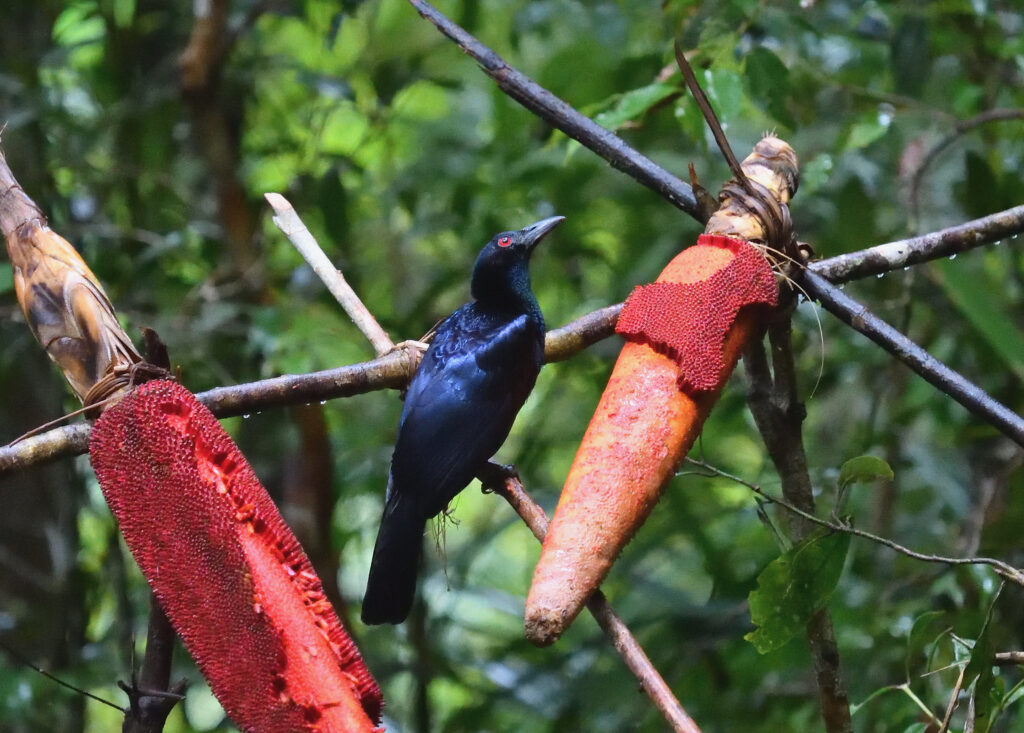

With its glossy black plumage and crinkled collar feathers, this bird performs elaborate courtship displays. Male manucodes dance and sing intricately to attract females during breeding season. Their lowland rainforest diet is fruits and insects. The crinkle-collared manucode mimicking other birds’ cries enriches the rainforest’s soundscape.
21. Crested Quail-Dove (Geotrygon versicolor)
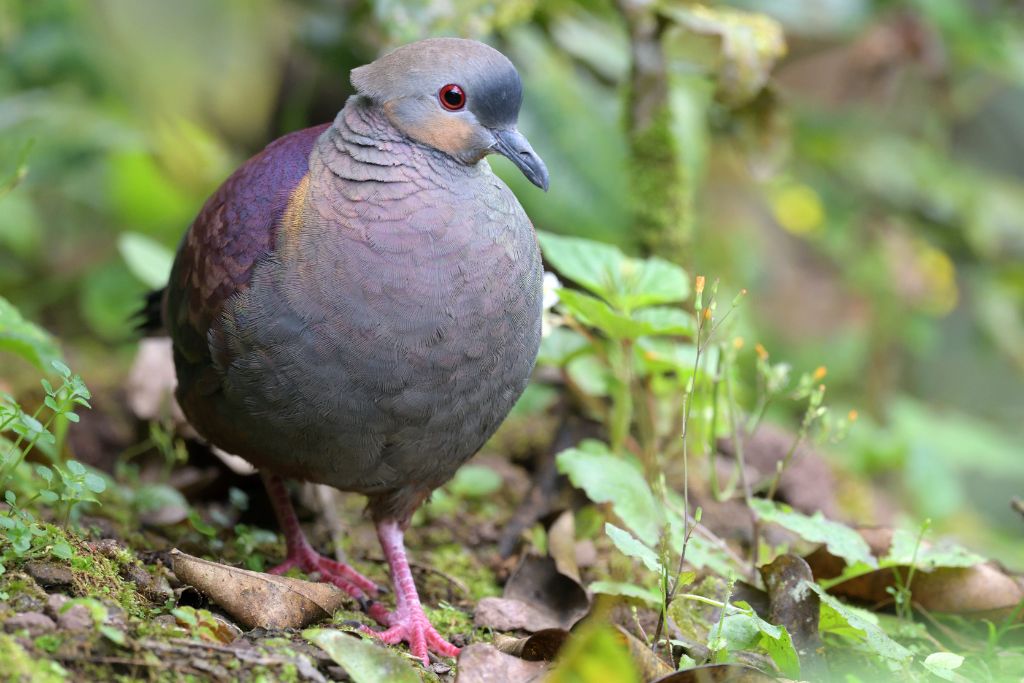

The crested quail-dove has beautiful, subdued plumage that can be seen in the Caribbean and Central America. Crest-topped doves have mild brown, gray, and lilac hues. They eat seeds, fruits, and insects in deep forests. They hide in the ground and coo delicately, making them hard to find. They replenish woodland vegetation by eating and depositing seeds.
22. Formosan Blue Magpie (Urocissa caerulea)
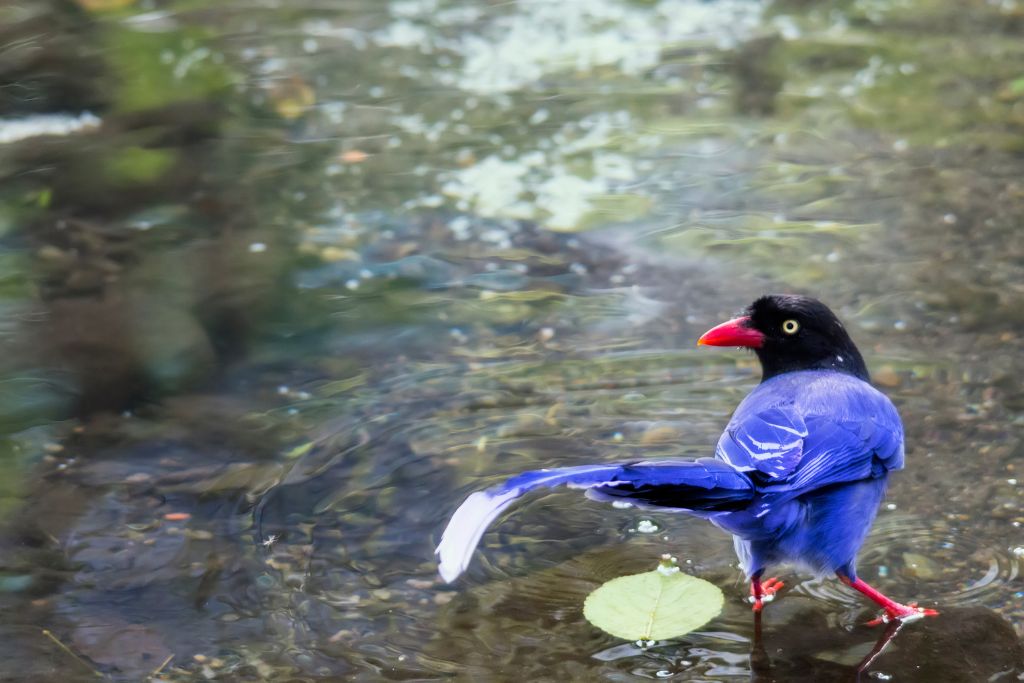

Taiwan has the stunning formosan blue magpie. This magpie’s bright blue plumage, long tail feathers, and black mask represent the island’s diversity. They play and mingle in evergreen forests. Collectively breeding families have sophisticated vocalizations. Smart magpies gather insects from tree bark with sticks. In Taiwan, formosan blue magpies signify nature.
23. Fork-Tailed Woodnymph (Thalurania furcata)
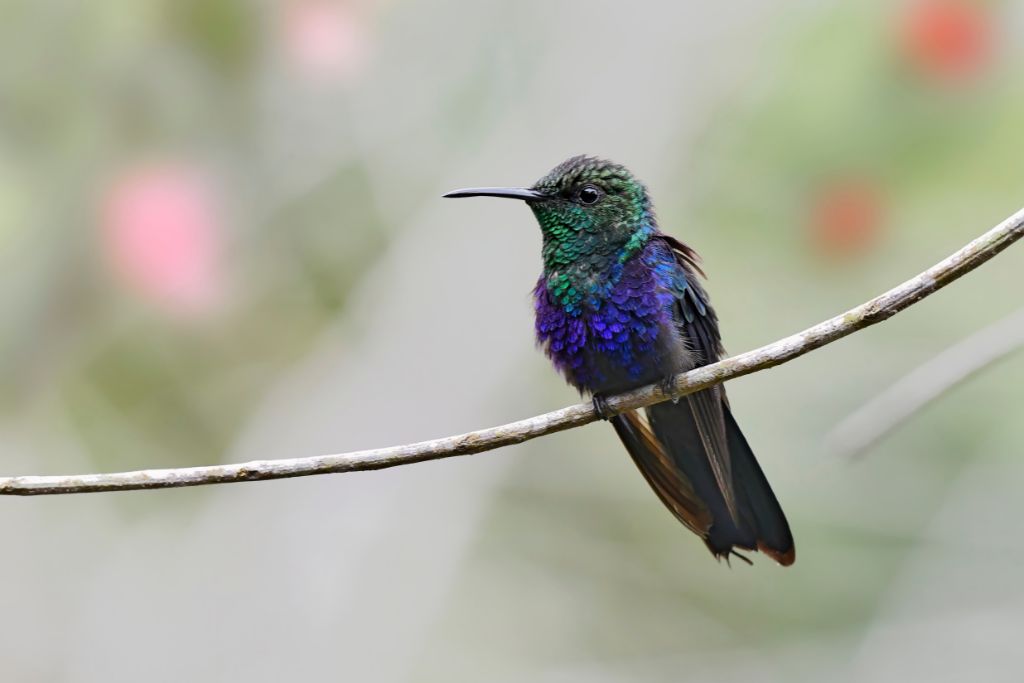

This swift, a bright green bird with long, forked tail feathers glides near flowers to drink nectar. In tropical and subtropical woodlands, the fork-tailed woodnymph pollinates flowers. Hummingbirds do flying tricks during courtship. Bright fork-tailed woodnymphs enhance environmental beauty.
24. Garnet Pitta (Erythropitta granatina)
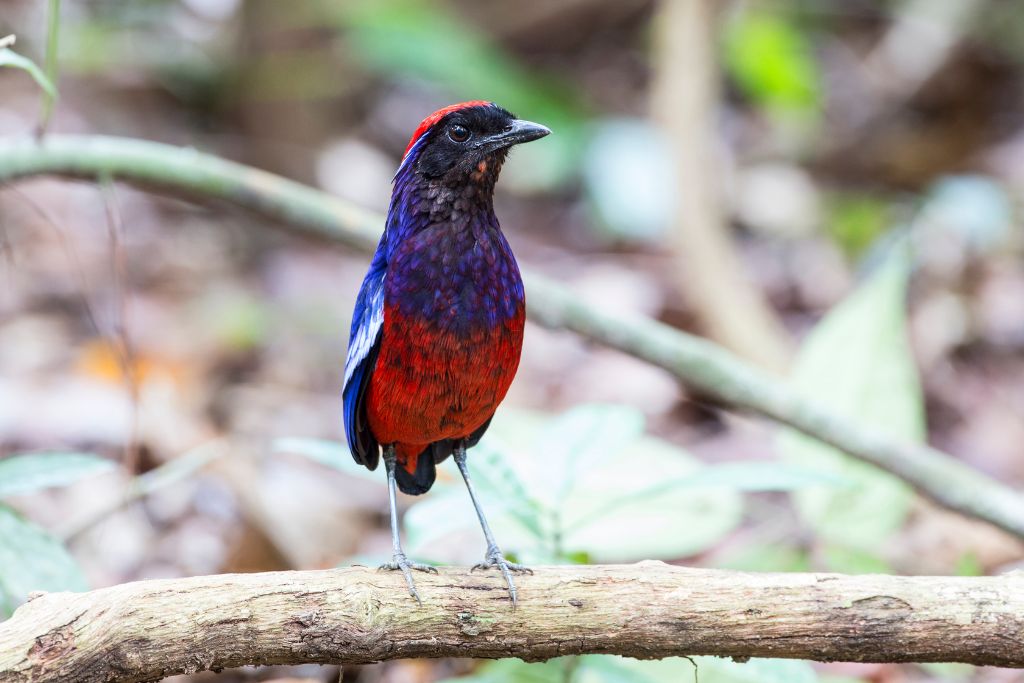

This pitta has a stunning blue crest and garnet-red plumage with black patterns. They lurk in foliage and are hard to spot despite their vivid coloration. They hop on the forest floor, collecting insects, invertebrates, and fruits. Malaysian and Indonesian lowland and montane forests host the garnet pitta.
25. Hartlaub’s Turaco (Tauraco hartlaub)

Hartlaub’s turaco is a unique bird of Central African woodlands and forests. This turaco is stunning with its emerald-green plumage, scarlet flight feathers, and white face band. Hartlaub’s turacos, known for their aerial tricks, fly through dense vegetation to find fruits, leaves, and insects. They inhabit lowland and montane forests in Uganda, Kenya, and Tanzania.
26. Indian Peacock (Pavo cristatus)
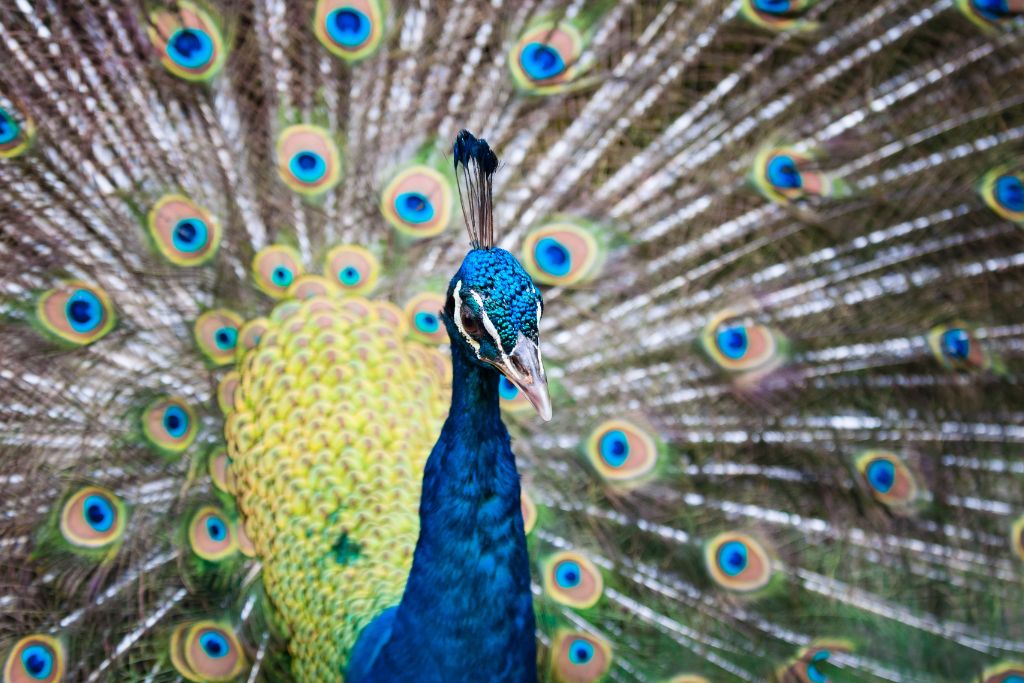

Male Indian peacocks have eye-shaped patterns, iridescent blue and green feathers, and a magnificent train of extended upper-tail covert feathers. Peacock males fan their tail feathers to impress females during courtship. Peacocks inhabit meadows, forests, and gardens in India, Sri Lanka, and surrounding countries.
Final Thoughts
Purple bird plumage captivates nature. Besides being beautiful, their colors help them choose partners and camouflage. Their distinctive traits may prompt purple bird conservation. Youth and adults are encouraged to enjoy these species, cooperating to protect and respect our feathered buddies and keep these beautiful purple birds painting the skies.
FAQs
How Rare are Purple Birds?
There aren’t that many purple birds in the world; only a few kinds have bright colors. On the other hand, you can find them in many places worldwide, showing how varied bird life is.
What is the Purple Bird Called?
The term “purple bird” refers to any bird with purple feathers. This is not a real bird called “the purple bird.” Some bird species, like the purple starling, purple martin, and purple honeycreeper, have feathers that are different shades of purple.





